With the rapid development of plastics industry technology, the current total output of plastics in the world has exceeded 150 million tons, and its use has penetrated into all sectors of the national economy and people’s lives. It has become the four pillar materials along with steel, wood and cement. . With the continuous increase in the production of plastics and the continuous expansion of its use, its waste is also increasing. Because they are difficult to be degraded and rotted in the natural environment or in the garbage yard after use, they become long-lasting and polluting the environment. According to statistics, the weight ratio of plastic in urban solid waste has reached more than 10%, and the volume ratio is about 30%. Most of them are disposable plastic packaging and daily necessities. Their pollution to the environment and ecological balance The destruction has caused great social concern. For this reason, efficient plastic recycling technology and research and development of degradable plastics have become important development strategies for the development of the plastics industry and the packaging industry, and have become a hot spot for research and development in the world.
The 1990s was an increasingly important era for the protection of the Earth's environment. It was an era in which resources and energy became more tense. We must ensure sustainable economic development, maintain a safe living environment for human beings, and clean living spaces. Countries around the world have environmental protection technologies and environmental protection products. Research and development have received great attention. To deal with the pollution of landscapes and ecological environment caused by large-scale, scattered, dirty, difficult to collect, or even forced collection of recycling, disposable plastic waste with little or no economic benefit, degradable plastic came into being. Gained faster development.
First, the classification, definition and use of degradable plastics
1, classification
There is no unified international standard for the classification of degradable plastics in the world. However, it can be used as a classification principle. From a practical point of view, classification based on the environmental conditions that cause degradation is more reasonable and easier to understand.
2, definition:
Degradable plastics have not yet reached a universal definition of international standardization in the world. However, the ASTM D883-92 standard for plastics terms adopted by the American Society for Testing and Materials (ASTM) defines a degradable plastic as follows: under specific environmental conditions, Chemicals that have undergone significant changes in structure and can be tested for changes in their material properties using standard test methods are basically consistent with the definition of degradation and degradation in ISO 472 (Plastics Terms and Definitions).
According to several international conferences and seminars, there are several ways to specify the definition of degradable plastics.
(1) Definition at the chemical (molecular level): The chemical structure of its waste has undergone significant changes, eventually degrading completely to carbon dioxide and water.
(2) The definition of physical property (material level): In the short term, the waste material loses its mechanical properties and most of its application function is lost.
(3) Morphological definition: The waste is broken, disintegrated, or powdered in a relatively short period of time. It becomes harmless to the environment or easily absorbed by the environment.
Table 1 Classification of Degradable Plastics
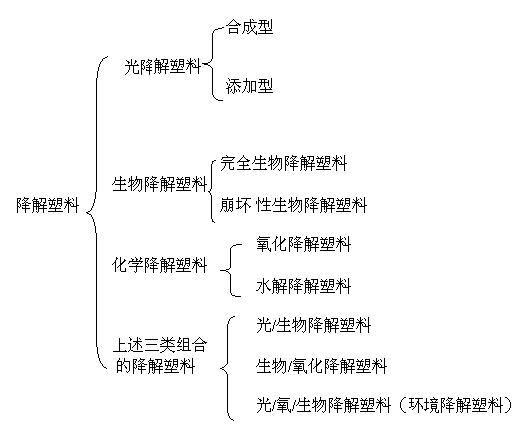
3, use
Degradable plastics are a new class of materials with a degrading function in the plastics family. Before or during use, they have similar or similar application performance and hygienic properties to similar plastics, and they can be used naturally after they have been used. Under the environmental conditions, it degrades quickly and becomes debris or crumb that is easily absorbed by the environment, and further degrades into CO2 and water over time, eventually returning to nature. Its uses include the following areas:
(1) Application of difficult-to-recycle areas in the natural environment
1 Agricultural materials: plastic film, nursery pot, pesticide and fertilizer slow-release materials, fishing nets, etc.
2 Civil and Construction Materials: Sections for the repair of civil engineering works in mountains and seas, water-proof sheets, vegetative nets, etc.
3 Buffer packaging materials for transport, launch products, sheets, plates, nets, ropes, etc.
4 Outdoor sports goods: disposable seats such as golf seats, fishing hooks, sea sports and mountaineering.
(2) Fields conducive to composting
1 Food packaging materials: food and beverage packaging films (bags), containers, food trays for Sages, and disposable fast food tableware.
2 Hygiene products: paper diapers, sanitary products, etc.
3 day groceries: light shopping bags, packaging films, shrink film, magnetic cards, garbage bags, cosmetics containers.
(3) Daily sundries:
1 disposable medical equipment:
2 medical materials: surgical sutures, drug release capsules, fracture splints, bandages and so on.
Portable Floor Projector screen
Portable Floor Projector Screen,Mobile Projection Screen,Fast Fold Projector Screen,Tabletop Portable Projector Screen
Dongguan Aoxing Audio Visual Equipment CO.,Ltd , https://www.aoxing-alr.com